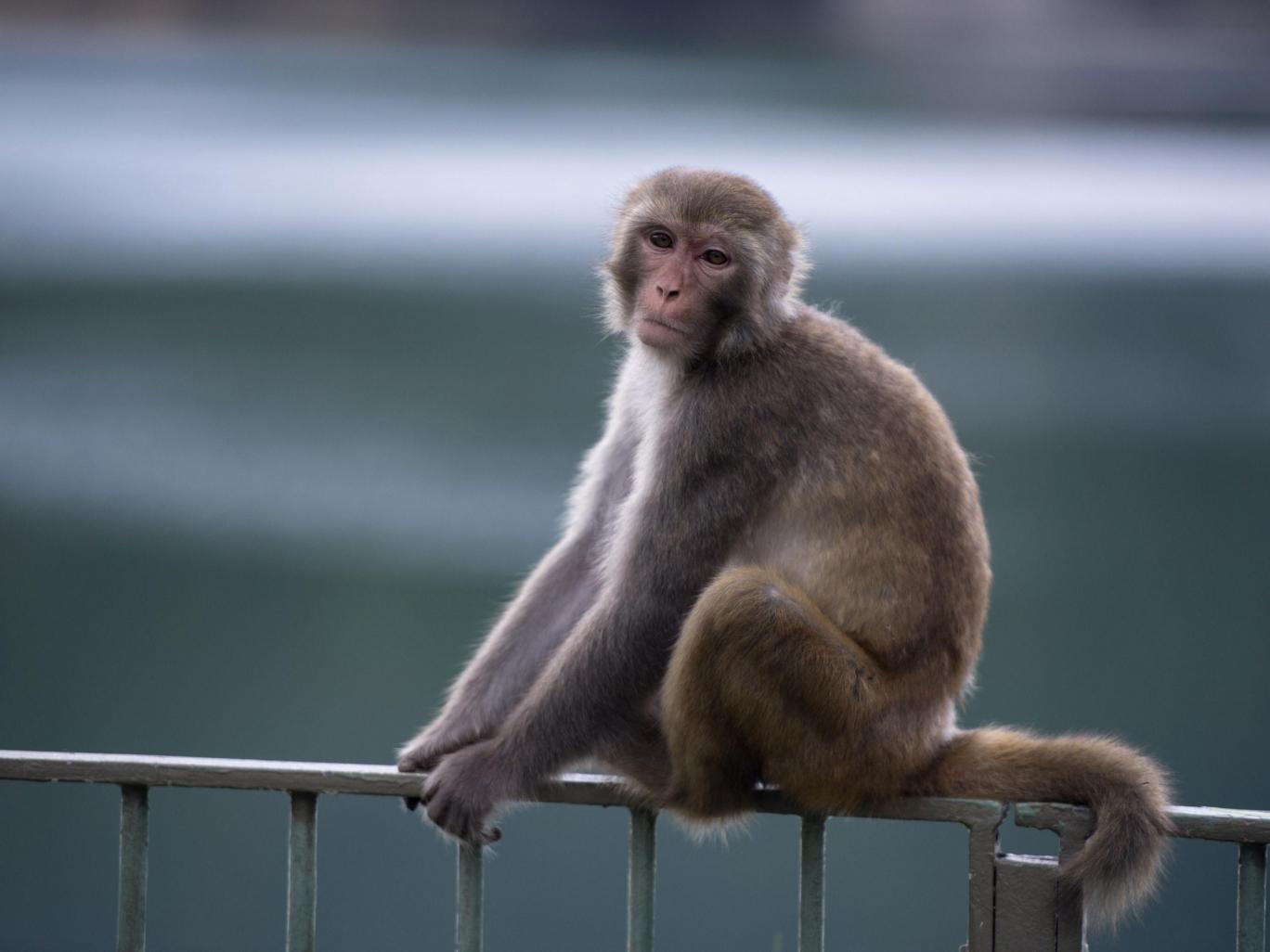
This meant they could serve as a reliable animal model for researching the causes of, and possible cures for, autism in humans -- a feat welcomed by other specialists not involved in the study.
"Our findings pave the way for the efficient use of genetically engineered macaque monkeys for studying brain disorders," the authors asserted.
Until now, animal studies of autism have relied mainly on lab mice -- a species very far removed from humans in terms of genes, behaviour and physiology.
So the team led by Zilong Qiu of the Institute of Neuroscience in Shanghai, created special test tube monkeys, giving them multiple copies of the MECP2 gene thought to be linked to autism in humans.
The monkeys were borne by surrogate females, and their behaviour studied as they grew up.
The researchers observed "an increased frequency of repetitive circular locomotion, increased anxiety, reduce social interaction", among other behaviours.
Humans can suffer a range of behavioural anomalies under the umbrella of autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Often sufferers are unable or unwilling to communicate or interact with others, sometimes cripplingly so.
Some patients have delays in cognitive development, whereas others can have dazzling gifts in fields such as maths or music.
The brain structure of autism sufferers is different to that of other people, but the exact cause or causes remain unclear, though genetics are strongly implicated.
There is no cure, and behaviour therapy is the main intervention.
- Passed on to offspring -
One of the monkeys transferred the transgene to its offspring, which also displayed autistic behaviour -- strengthening the hypothesis of a genetic root for autism, the study authors said.
Qiu said the team would now scan the brains of their monkeys to try and identifiy circuit deficiencies.
"Once we identify this brain circuit (problem) associated with the autism-like behaviour, we will use therapeutics such as gene editing tools... to manipulate this MECP2 transgene in the transgenic monkey," he explained.
They could then begin to test potential treatments in the macaques -- members of the closely-related primate family -- a first step towards a possible human drug or therapy.
Qiu insisted the team's methods met international ethical standards.
Other scientists hailed the study as an "exciting development".
"Developing sophisticated animal models of autism has always represented a significant challenge for scientists," said James Cusack, research director at the autism charity Autistica.
"This excellent research has developed a more sophisticated model of autism which may further our understanding of autism and could eventually lead to the development of more tailored treatments," he said through the Science Media Centre.
University of California psychiatry professor Melissa Bauman said the work "opens the possibility to explore genetic risk factors in a species more closely related to humans."
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"Our findings pave the way for the efficient use of genetically engineered macaque monkeys for studying brain disorders," the authors asserted.
Until now, animal studies of autism have relied mainly on lab mice -- a species very far removed from humans in terms of genes, behaviour and physiology.
So the team led by Zilong Qiu of the Institute of Neuroscience in Shanghai, created special test tube monkeys, giving them multiple copies of the MECP2 gene thought to be linked to autism in humans.
The monkeys were borne by surrogate females, and their behaviour studied as they grew up.
The researchers observed "an increased frequency of repetitive circular locomotion, increased anxiety, reduce social interaction", among other behaviours.
Humans can suffer a range of behavioural anomalies under the umbrella of autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Often sufferers are unable or unwilling to communicate or interact with others, sometimes cripplingly so.
Some patients have delays in cognitive development, whereas others can have dazzling gifts in fields such as maths or music.
The brain structure of autism sufferers is different to that of other people, but the exact cause or causes remain unclear, though genetics are strongly implicated.
There is no cure, and behaviour therapy is the main intervention.
- Passed on to offspring -
One of the monkeys transferred the transgene to its offspring, which also displayed autistic behaviour -- strengthening the hypothesis of a genetic root for autism, the study authors said.
Qiu said the team would now scan the brains of their monkeys to try and identifiy circuit deficiencies.
"Once we identify this brain circuit (problem) associated with the autism-like behaviour, we will use therapeutics such as gene editing tools... to manipulate this MECP2 transgene in the transgenic monkey," he explained.
They could then begin to test potential treatments in the macaques -- members of the closely-related primate family -- a first step towards a possible human drug or therapy.
Qiu insisted the team's methods met international ethical standards.
Other scientists hailed the study as an "exciting development".
"Developing sophisticated animal models of autism has always represented a significant challenge for scientists," said James Cusack, research director at the autism charity Autistica.
"This excellent research has developed a more sophisticated model of autism which may further our understanding of autism and could eventually lead to the development of more tailored treatments," he said through the Science Media Centre.
University of California psychiatry professor Melissa Bauman said the work "opens the possibility to explore genetic risk factors in a species more closely related to humans."
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------









 Home
Home Politics
Politics