The findings in the journal PLOS ONE suggest his maternal lineage likely came from the north Mediterranean coast, on the Iberian Peninsula, perhaps near what is modern day Spain or Portugal.
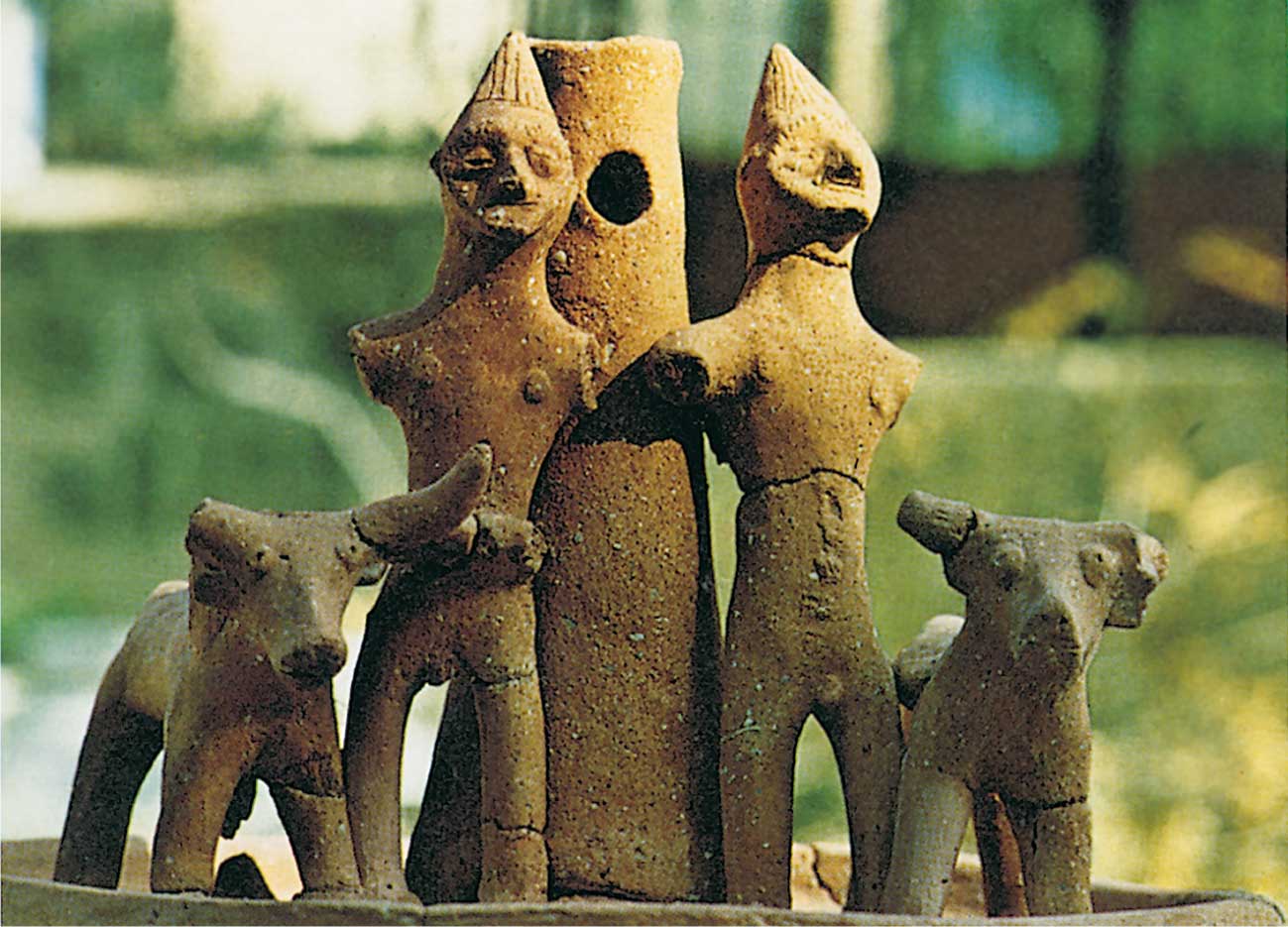
Phoenicians are known as the creators of the first alphabet, and inhabited the coastal cities, Tyre, Sidon, Byblos and Arwad, in what is now Lebanon and southern Syria.
However, since their writings were made on papyrus, little remains except what has been written about them by Greek and Egyptian scholars.
According to lead study author Lisa Matisoo-Smith, a professor in the department of anatomy at New Zealand's University of Otago, the remains reveal the earliest known evidence in North Africa of a rare European genetic population, or haplogroup, known as U5b2c1.
"U5b2c1 is considered to be one of the most ancient haplogroups in Europe and is associated with hunter-gatherer populations there," she said.
"It is remarkably rare in modern populations today, found in Europe at levels of less than one percent."
The matriarchal DNA of the man, whose remains were found by gardeners working outside the National Museum of Carthage in 1994, "most closely matches that of the sequence of a particular modern day individual from Portugal," she added.
The discovery sheds some new light on the history of the Phoenicians, who are thought to have originated in Lebanon and spread across the Mediterranean.
Carthage was a prominent Phoenician port and trade center established by colonists from Lebanon.
However, researchers were unable to find any links between the ancient man's mitochondrial DNA and that of 47 modern Lebanese people who were analyzed for the study.
"Hopefully our findings and other continuing research will cast further light on the origins and impact of Phoenician peoples and their culture," said Matisoo-Smith.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Phoenicians are known as the creators of the first alphabet, and inhabited the coastal cities, Tyre, Sidon, Byblos and Arwad, in what is now Lebanon and southern Syria.
However, since their writings were made on papyrus, little remains except what has been written about them by Greek and Egyptian scholars.
According to lead study author Lisa Matisoo-Smith, a professor in the department of anatomy at New Zealand's University of Otago, the remains reveal the earliest known evidence in North Africa of a rare European genetic population, or haplogroup, known as U5b2c1.
"U5b2c1 is considered to be one of the most ancient haplogroups in Europe and is associated with hunter-gatherer populations there," she said.
"It is remarkably rare in modern populations today, found in Europe at levels of less than one percent."
The matriarchal DNA of the man, whose remains were found by gardeners working outside the National Museum of Carthage in 1994, "most closely matches that of the sequence of a particular modern day individual from Portugal," she added.
The discovery sheds some new light on the history of the Phoenicians, who are thought to have originated in Lebanon and spread across the Mediterranean.
Carthage was a prominent Phoenician port and trade center established by colonists from Lebanon.
However, researchers were unable to find any links between the ancient man's mitochondrial DNA and that of 47 modern Lebanese people who were analyzed for the study.
"Hopefully our findings and other continuing research will cast further light on the origins and impact of Phoenician peoples and their culture," said Matisoo-Smith.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------









 Home
Home Politics
Politics