Lessing was a member of the Communist Party in the British colony of Rhodesia -- modern-day Zimbabwe -- where she grew up with her English parents.
The security services found no evidence that she joined the British wing of the party after moving to London in 1949, although she was actually a member between 1951 and 1956.
A 1952 memo from the MI6 foreign intelligence agency described her as "certainly pro-Communist, though it is doubtful she is a member of the party."
"Her communist sympathies have been fanned almost to the point of fanaticism by her upbringing in Rhodesia," it added.
"Colonial exploitation is her pet theme... saying that everything black is wonderful and that all men and all things white are vicious."
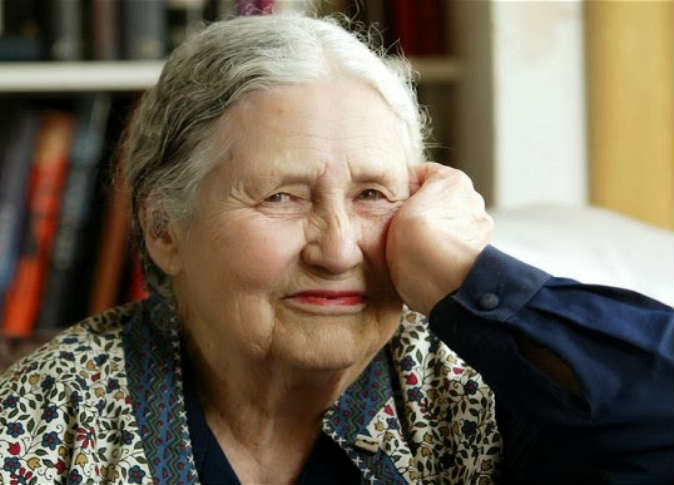
Lessing died in 2013, aged 94, and is renowned for her powerful feminist and anti-colonial writing.
Best known for the 1962 novel "The Golden Notebook", today considered a landmark feminist work, Lessing became the oldest winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2007, just shy of her 88th birthday.
She penned more than 50 other works ranging from political critiques to science fiction -- many of them inspired by her own experiences of a lonely childhood in Africa and involvement in radical leftist politics.
After running away from her second husband and moving to Britain in 1949, she became involved in the British Communist Party, but resigned in 1956 at the time of the Hungarian uprising, which was crushed by Soviet tanks.
She had previously been impressed by her visits to Joseph Stalin's Russia, according to the archives.
Information gathered by colonial intelligence services said she spoke of the "superiority of living conditions and educational development in the Soviet Union compared with other European countries and Africa."
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The security services found no evidence that she joined the British wing of the party after moving to London in 1949, although she was actually a member between 1951 and 1956.
A 1952 memo from the MI6 foreign intelligence agency described her as "certainly pro-Communist, though it is doubtful she is a member of the party."
"Her communist sympathies have been fanned almost to the point of fanaticism by her upbringing in Rhodesia," it added.
"Colonial exploitation is her pet theme... saying that everything black is wonderful and that all men and all things white are vicious."
Lessing died in 2013, aged 94, and is renowned for her powerful feminist and anti-colonial writing.
Best known for the 1962 novel "The Golden Notebook", today considered a landmark feminist work, Lessing became the oldest winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2007, just shy of her 88th birthday.
She penned more than 50 other works ranging from political critiques to science fiction -- many of them inspired by her own experiences of a lonely childhood in Africa and involvement in radical leftist politics.
After running away from her second husband and moving to Britain in 1949, she became involved in the British Communist Party, but resigned in 1956 at the time of the Hungarian uprising, which was crushed by Soviet tanks.
She had previously been impressed by her visits to Joseph Stalin's Russia, according to the archives.
Information gathered by colonial intelligence services said she spoke of the "superiority of living conditions and educational development in the Soviet Union compared with other European countries and Africa."
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------









 Home
Home Politics
Politics